The First Moment of Creation and the Nature of Time, Dark Energy and Dark Matter
Malcolm McCoard

The First Moment of Creation and the Nature of Time, Dark Energy and Dark Matter
Malcolm McCoard
Independent researcher, Ayr, Scotland
Email: thedelitroon@hotmail.co.uk
Copyright © 27th July 2025 by Malcolm McCoard
This license allows users to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for non-commercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creator. If you remix, adapt, or build upon the material, you must license the modified material under identical terms.
Abstract
If we understood the first moment of creation, would that provide a blueprint for everything that followed? Whatever ‘structure’ or forces were at play in that moment, must determine every aspect of our reality. Any such proposition is necessarily highly speculative. However, if the model created, closely matched our reality and provided cause-and-effect insight into the mysteries of time, dark matter, dark energy and gravity, would it not justify proper scientific scrutiny? This article presents a strong candidate for that first moment. One that starts with nothing; no dimensions or primordial energy. Yet must logically create a stable, infinite universe of balanced energy orbits, oriented at 90 degrees, mirroring string theory. The basic energy structure formed, by a single fundamental force towards reconciliation of dimensionally offset orbits, when propagated and aligned, creates dimensions, electromagnetic and mass bearing Higgs' fields. Exponential reciprocal forces predicted, must logically end inflation, in a modified big bang. Creating an infinite universe but under massive compression. The resultant fragmentation of these structures creates matter and radiation to the same blueprint. Time dilation now applies to spacetime moments released from this compressed state. This constant time dilated release and expansion of spacetime moments, after an initial hot big bang, allows cause to move to effect across the entire universe, explaining both time and dark energy. Gravity from spacetime energy compressed along the temporal plane, yet to be released, we call dark matter. Further consistent conjecture on gravity, force carrying virtual particles and even quantum entanglement is presented.
Keywords
Time, Dark Energy, Dark Matter, Creation, Big Bang, Forces, Gravity
1. A Broken Universe
The universe, or rather our current understanding of it, is broken. Between unseen dark matter and unexplained dark energy, over 95% of everything in the universe is missing [1]. In the most widely accepted theory of creation; the big bang, a possibly infinite universe with ready-made spacetime dimensions just appears out of nothing or from unexplained primordial energy [14]. Cause-and-effect and common sense are all but abandoned in the quantum world. Forces are carried by messenger particles which spontaneously appear and disappear [1], but then what actually holds these fundamental particles together? Universal gravity, the nature of time, anti-matter asymmetry and the apparent ‘magic’ of quantum entanglement, just add to our discomfort. Like a jigsaw puzzle, where some of the key pieces are missing or misaligned. Large sections look correct in isolation, but the overall picture no longer makes sense. Unravelling a universe of unimaginable complexity is of course, incredibly difficult. However, what if we started somewhere inherently simpler; at the very beginning? So, I’ll kick things off with a philosophical question:
Such a starting point, is by its very nature, speculative and difficult, if not impossible to prove. However, if the universe had a beginning, there can be only a finite number of credible scenarios. Only one will offer a perfect fit and solutions for the problems listed above, the correct one. Let me be clear from the start, this article is philosophical in nature. I will present no new mathematical framework or proof. I will however present a strong candidate for that first moment. One which, unlikely as it sounds, provides an extraordinary and consistent cause-and-effect explanation for why our universe behaves the way we observe it. The proposition presented does not change existing frameworks. Instead, it proports to align with and explain why many of our current models work. My hope is that the model presented will demand closer scrutiny by the wider scientific community and inspire others with the required skills to develop this proposition into a more robust scientific theory.
There are necessarily a few paradigm shifts required, especially early on, so please bear with me and try to keep an open mind. The fit, once all the pieces fall into position, is compelling. “We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them,” Albert Einstein.
2. Something for Nothing
This model starts with a modified big bang. One that crucially starts with absolutely nothing. No time, no energy, no dimensions or forces. The big zero. It is difficult to even imagine. We know only one thing about it for certain. We are here, so at some level, this condition was unstable. It follows that there must have been a change or a rift in this condition. Whatever comes next, must therefore also sum to zero, otherwise we have an unexplained and infinite energy imbalance. Positive something and negative something, that sum to zero (not infinity as most current theory suggests):
0 = +1 add -1 (1)
In our universe, the most basic component of creation is energy. Negative energy, to balance our equation, I have to admit is highly speculative. However, without it we must abandon both the law of conservation of energy and also basic mathematics. So, I ask you for some latitude here and perhaps ‘everything’ will actually start to make sense. In the first ‘quantum fluctuation’ to create +1 and -1, a pull towards reconciliation or cancellation is logical. If we have any type of separation, then there is a debt to be repaid. Except, as our universe exists, there can be no such reconciliation. Therefore, -1 and +1 must be offset in some way, so that they cannot meet and cancel.
Crucially, we have no dimensions yet, so the point of creation must, by definition, be dimensionless. What is a dimension, if not the alignment of energy along a common axis? So, this first quantum fluctuation has actually created the first two fledgling dimensions. However, being dimensionally offset, they can never meet. Spatial dimensions are squeezed together with immense forces inside massive stars and when falling into black holes, they bend but never meet. Einstein’s model of gravity tells us that spacetime dimensions may become distorted, but they do not collide.
This model postulates that there is one fundamental force in our universe, which is simply the pull towards reconciliation from dimensionally offset positive and negative energy [2]. I aim to demonstrate, cause-and-effect, how such a single unifying force, could create all the other ‘fundamental’ forces; from inertia and gravity, to generating messenger particles, responsible for carrying the electromagnetic force and imparting mass. But we have a long way to go. First on a substantial hit list; dimensions.
3. Dimensions
Any geometry teacher will tell you, that any line (and therefore trajectory of energy) leaving from a point or sphere, comes at 90 degrees from a tangent to its surface. Refer to Figure 1 below.
If we start from a dimensionless point, then energy could create any number of dimensions, all at 90 degrees to this point and therefore each other or they can be diametrically opposed. We can see this in spatial dimensions, but also electrical and magnetic forces, which are also offset by 90 degrees.
4 Balanced energy-force orbits
Logically, what happens next, is repeated time and time again, both on the smallest and largest scales in our universe. Energy affected by a dimensionally offset force, will follow a stable orbit, unless acted on by another force. Planets orbit the sun, due to gravity pulling along an offset temporal plane. Orbits can be a circle, an ellipse or even a pendulum motion, however they all exhibits very special properties. Firstly, there is always a change in angular momentum, at every point along their trajectory. Perhaps echoing Newton’s second law [4], where the change in momentum of mass, is always accompanied by a force? Mass is itself, a form of energy according to Einstein’s most famous equation [3]. In equation 2 energy, e equals mass times the speed of light, c squared.
e=mc2 (2)
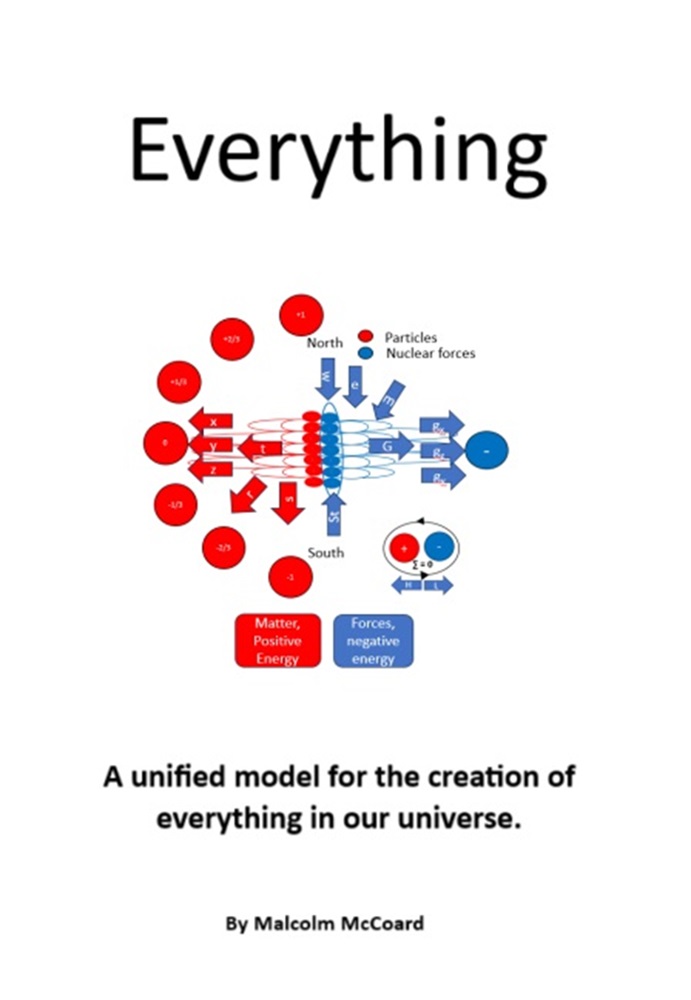
Secondly, the forces acting at any point on this trajectory are balanced. Orbits are completely stable. In the energy orbits proposed, the outward pull of angular momentum, is matched by an inward pull towards reconciliation. Two dimensionally offset and stable orbits are therefore created. Positive energy feels a pull towards reconciliation through the dimensionless point to its negative energy twin and vice versa. I will use negative energy and force interchangeably, as with this proposition, force is how we experience the effects of negative energy, and its pull towards reconciliation, within our positive spatial dimensions. These balanced force-energy orbits, I am proposing are the most basic building blocks of our universe; composing both dimensions, the structure of spacetime and when stabilized and locked in place by nuclear forces, under extreme compression to form matter. Refer to Figure 2a and b below.
On the LHS positive energy (red) and negative energy (blue) orbit a common dimensionless point, the black dot. At any point along their orbits, there is a pull towards reconciliation through the dimensionless point, the orientation of which is constantly changing, thus creating a stable concentric force towards the dimensionless point. Any other energy or particle we introduce within this ‘sphere’ of influence is therefore also deflected by this force. Spin an object on a string around your hand and you will feel this change in angular momentum. Spin it fast enough, there is a seemingly constant concentric pull. The RHS is a simplified 2-dimensional representation, left is positive energy and right is negative energy or force. Energy and force are simply two sides of the same coin. In a universe composed of such orbits, if we push an object (presumably composed of other smaller more concentrated spatial energy orbits) in any direction, energy moves in opposition to the force acting towards dimensionless points in that plane and a reciprocal force pushes back. This reciprocal force, provides a basis for the force we call inertia, but there will be more to the associated property of mass in this model, as there is in conventional field theory [9]. Movement of energy or mass in such a universe must create a reciprocal force [2].
However, if this were the case, where is this energy movement when we come to other forces like gravity? These days we have established that dark energy is expanding our universe everywhere [1], so there is now a potential answer. Expansion of spacetime everywhere, if created to the same energy blueprint, would create a universal force, pulling on all similarly dimensionally aligned energy orbits back in the opposite orientation to its expansion, a reciprocal force pulling all such orbits together against this expansion. Potentially offering a basis for universal gravity for the first time?
Hopefully I’ve moved you some
way from the; “What’s this nonsense box?” towards the “Actually, this may offer
some potentially interesting synergies with our reality, but I’m far from
convinced,” box. So, let’s think about how such a universe would develop. There
is no time yet, we have not yet created movement along a temporal plane, if
indeed, that is what time is. Even if one of these orbital trajectories was
along the temporal plane, there is no resistance to energy movement within any
orbital plane, so these energies must move at infinite speed. There is however,
still cause-and-effect. Refer to Figure 3 below A multidimensional energy-force
structure develops
Otherwise, there is no order, only chaos. So, energy drawn in any plane, must instantaneously return to its point of origin. In doing so, both energies return to the exact conditions present during the first quantum fluctuation. Logically, what happened in that first ‘instant’, must now repeat and energy is once again drawn from this rift to the same blueprint. As this process is instantaneous, energy is effectively drawn continuously.
These original orbits must be or will become full. Additional energy must therefore either create a new dimensional orbit or another concentric orbit in the same dimensional plane. Akin to adding another line of force to a magnetic field. A multi-dimensional structure of concentric energy orbits must result, shown simplified in 2 dimensions in Figure 3. I have shown concentric orbits with a single line for clarity. Whenever we add another orbit in the same plane, you increase the concentric pull on any energy within these orbits. Like turning the power up on an electromagnet. Stronger magnets have more concentric lines of force. We have created a continuous and potentially infinite energy engine, breaking 0 into +1 and -1. Propagate this structure, which with continuous energy flow is to be expected, and an infinite stable universe is the logical outcome. A cosmos where such structures must align along dimensional energy planes to create familiar dimensions. An infinite but stable universe, created from absolutely nothing, where the sum of all energy and forces is always zero. A zero-sum universe [2].
The proposition is that some of these dimensions will develop into our familiar spatial dimensions, their energy providing the basis for the mass giving Higgs' field [9]. Others will create electrostatic and magnetic dimensions or fields and their familiar associated electromagnetic forces. I will also propose that there will be other much smaller and stronger ‘dimensions.’ These energy shells and their matching forces will be responsible for particle formation under the extreme compression, which as we will soon demonstrate, must now follow in such a universe.
5 Dimensional planes
I have been talking about orbits in a single dimension, however unless orbits are pendulum-shaped they are actually circles or ellipses in 2-dimensions. Spatial dimensions have width and depth, or width and height or depth and height. Our spatial dimensions are therefore linked through shared dimensions to form 3-dimensional space. Similarly, the electrical and magnetic dimensions are, I believe, similarly linked to form a plane with 2 dimensions at 90 degrees to each other. This plane will likely be smaller, stronger and may therefore be fully encompassed within our spatial dimensions. Electrostatic and magnetic dimensions do not share any common spatial dimension, they are therefore fully independent of spatial dimensions. You can create a magnetic force at 90 degrees to the flow of an electric current in a wire and rotate that wire to any spatial orientation. The magnetic force is still at 90 degrees to the flow of electricity. I will continue to talk about orbits in a single dimension, this is because our focus here is on the dimensions and forces, which they will create through their alignment.
6 String Theory
A universe composed of orbits or loops of energy is actually fully aligned with current thinking. String theory is a theoretical framework which tries to describe the behaviour of the universe on the quantum scale. It uses single dimensional energy rings, called strings, which travel through space rather than point-like particles to explain behaviour at a subatomic or quantum level [5]. These strings vibrate at different characteristic frequencies. These correspond to different properties like charge or mass. I will later disagree somewhat with this last assertion. They will have different characteristic frequencies yes, but I believe these are as a result of their charge or mass. If you observe a string of a particular length, pinned at each end it will display a limited number of vibrational patterns or states, based on the energy it possesses. There is an obvious synergy between string theory and the one I am suggesting, they both involve multi-dimensional energy rings. However, with a universe based on paired opposite energy and dimensionally separated orbits, we actually understand why such energy strings exist as stable energy orbits or strings. They are bound together by a concentric force towards their dimensionless point, which matches the outward force due to their angular momentum. They don’t just simply exist because the maths works and we can model our universe on that basis.
There is a further advantage with this model. In the analogy above, the strings had to be pinned at either side to vibrate in these characteristic patterns. They need to be under tension or they would simply bounce off each other, spin away from each other or buckle. Paired energy orbits mean that these energy orbits are always under tension, being pulled around in a stable orbit by their negative energy twin, focused around a dimensionless point. They will therefore adopt characteristic vibrational frequencies, when interacting with other dimensional energies or attaining a certain energy through collisions. The model I am suggesting is, I believe, entirely compatible with string theory at its most fundamental level. It provides an explanation of why we can describe our universe mathematically on this scale using strings of energy. If the universe is not fundamentally composed in this manner, why would string theory work at all?
7 Spacetime Properties and Mass
Before we delve into the development of structure and propagation of this basic energy unit. Let’s consider further the properties of a universe, such paired balanced forced energy orbits, would create. Einstein showed that all matter was energy, all matter occupies 3-dimensions, in this model it therefore has stable energy orbits aligned in spatial dimensions. Matter also holds massive amounts of energy, shown by Equation 2. So, it is only logical to suggest that such matter, would be highly compressed when compared to that which I am contesting makes up dimensions and the relative ‘vacuum’ of space. Notice, if we compress paired energy orbits, we also compress the force side. If we somehow lock orbits into new smaller and therefore stronger orbits, for example by compressing them within other stronger orbits. We would then have a basis for the formation of stable matter particles or radiation, forged within the massive energy of the hot big bang.
If we consider an established universe and throw in a single particle with mass. For simplicity, we will consider only one dimension. It will exist as a tiny energy orbit within another much larger dimensional energy orbit. We have just added the concentric pull of both orbits together. Pulling all energy within this ‘sphere’ of influence of this single fundamental force, with a stronger combined pull towards their concentric dimensionless centres. The result; compression of both energy orbits. This provides us with a cause-and-effect explanation of why matter compresses spacetime (and also any matter present). We now have a basis for Einstein’s compression of spacetime by matter. Something current theories lack. A fundamental force towards reconciliation, now explains Einstein’s curvature of spacetime. I am going to refer to this as gravity+. It does not yet provide the second force necessary to explain gravity fully; the force pulling all energy and matter together everywhere and instantaneously, universal gravity, although I dropped a big hint earlier.
Move the same matter particle onwards through spacetime and both the particle and background dimensional orbits must simply return to their original trajectories; those set by their energy and the compression of their paired force orbit. There is no locking in of this gravity+ compression. Spacetime and matter are fully compressible without energy input to expand or contract it. This matches the behaviour of spacetime, as seen, whenever a planet or other massive object moves through it.
All energy orbits are full and / or dimensionally offset. We have a concentric force which will act on any energy within the local ‘sphere’ of influence of its paired negative energy. This will act to deflect other positive or negative energy orbits which come into their proximity. Orbits are full and will never collide, even those in the same dimension. There will only be deflection. Deflection of energy orbits between other orbits, must result in compression into relative peaks and troughs of energy or waves within any given dimension. The result of innumerable such interactions, as we would expect from more complex multi-particle and multi-dimensional interactions, would be predictable only by probability. Waves of energy are created by deflection, but there is no energy bow wave pushed ahead of particles resisting their movement through spacetime. Again, an excellent fit with the observed properties of spacetime. In such a universe a photon of light, were it to possess electromagnetic energy within orbits, would continuously create deflections; waves in a background electromagnetic dimensional energy field, without itself being slowed. Which of course they do.
Deflections from any spatial plane (e.g., length and breadth) between particles and any background dimensional orbits would create a change in energy momentum in the third spatial dimension (depth) and with it, reciprocal forces must be created. Deflected energy must return to its equilibrium orbital trajectory, so such forces act both in and out of each spatial dimension. In this way we would expect all particles with spatial orbits to be cocooned in spatial energy and balanced inertial forces but also localized concentric compression. These deflections will magnify the energy in any plane and therefore any reciprocal forces created by movement; inertia. Particles with spatial orbits, therefore interact with a background energy field everywhere, imparting a property we might recognize as mass. We have essentially created what conventional physics calls the Higgs' field [9], but as yet without the messenger particle; the Higgs' boson, reputedly responsible for its creation. This particle and other force carrying particles will also be logical conclusions of the model I am proposing, but as an effect within, not the cause of this field.
So, a universe based on paired energy-force orbits, so far has an excellent fit with the observed properties of spacetime. It is creating familiar properties, as a result of cause-and-effect and potentially provides new insights into universal gravity and spacetime compression, which conventional models do not explain. Starting to get interesting? Perhaps, but I believe that we have yet to scratch the surface of its full potential.
8 Energy momentum and forces; Newton’s second law.
Consider an established universe created to this blueprint, one in which there is expansion everywhere; fuelled by so called dark energy. Again, a single dimension will do. Expansion entails movement of spatial energy relative to the sphere of influence of existing negative energy orbits. A reciprocal force, one acting against the direction of movement of that energy movement, is therefore experienced by any other energy orbits present. In an established universe, expansion in all spatial dimensions everywhere must create a reciprocal force acting in opposition to that movement. This, coupled with the energy movement associated with dark energy expansion, provides us with a cause-and-effect explanation for instantaneous universal and quantum gravity. The otherwise unexplained gathering of all matter and energy together at distances well beyond which Einstein’s curvature of spacetime can explain [2,14].
If you concentrate up these energy orbits into something we call matter and give it a push, the much larger reciprocal force created, is what we call inertia. The mass, as we discussed in the previous section, being a product of inertial reciprocal forces from both the movement of the orbit and any deflections with background dimensional orbits. The greater the mass or energy present, the greater the inertia. Stop the movement and no inertial force applies. This creates the basis for the second equation needed to create our universe, Newton’s second law:
F = ma (3)
or force F, equals mass m, times acceleration a. Commonly expressed as: ‘any change in the movement or momentum of matter requires an equivalent force’. I am however going to refine that slightly, on the basis of the model presented and Einstein’s interchangeability of energy and matter to:
Any change in the momentum or movement of energy, always creates a corresponding reciprocal force.
There are profound implications of this rule for the big bang and for our understanding of time itself. I am going to propose that inflation, the infinite expansion of the universe [12] is actually infinite propagation of the energy structure, which we started to build earlier [2]. This makes a lot of sense when we think of black holes. Black holes compress spacetime back towards a singularity or dimensionless point at any point in space and time, not back to a single central point and time. With this model the infinite expansion of inflation must also create exponential growth of reciprocal forces, in every dimension. An infinite universe is still created, but created under conditions of increasingly extreme compression. Just the compression we would need to forge tiny powerful energy orbits we might call matter and radiation from the energy orbits we are creating. The current big bang theory offers no explanation of why inflation stops… it just does. Again, this model of the universe can offer cause-and-effect, where conventional theory describes only effects. It will be the massive deceleration and compression due to the exponential reciprocal dimensional forces created, that both stops inflation and instigates the hot big bang.
9 Structure Development - Introducing the Quantum Pole
If we recall the basic energy structure developed earlier from these paired energy-force orbits. Parallel concentric orbits in each plane were shown as a single line in Figure 2 above. We know that forces in our universe are not of equal strength – a magnet can raise a pin off a table, outgunning the gravitational pull of the whole planet. So, structure must develop within these multi-dimensional energy ‘spheres,’ such that there is a variation in their corresponding force strengths. I will give you my best guess, as to how such structure might develop and eventually propagate. It is logical, though probably highly simplified and there are potentially many alternatives. If this overall model is accepted, this will certainly be challenged and refined. However, the outcome I will propose, aligns well with the universe around us. I would regard the process described as illustrative, however I believe the results, in the context of the energy orbit model proposed, can provide further insight into our reality at a fundamental level.
Electrostatic and magnetic orbits and their associated force orbits are denoted e and m, in Figure 4 respectively. I expect these to be mirrored on either ‘hemisphere’ of this structure. The energy orbits responsible for developing into our spatial dimensions are denoted x, y and z, with their corresponding reciprocal gravitational / inertial forces gx, gy and gz. I believe that those orbits closest to the dimensionless point will become the strongest, simply due to their proximity to the dimensionless point. These strongest orbits, I will later propose, will be responsible for particle formation and with massive compression create our nuclear forces. Then the electrostatic, e and magnetic, m orbits and finally the weakest, the spatial orbits. This may simply be due to congestion of energy orbits around the dimensionless point, squeezing some orbits outwards whilst others are pushed and compressed inwards into closer stronger orbits.
As concentric orbits are added in all planes, congestion will also build on the return orbits towards to the dimensionless point. With increased congestion at the centre, the return paths of the electrostatic and magnetic orbits logically will become choked. See Figure 4 External electromagnetic orbits develop due to congestion.
Orbits develop instantaneously but sequentially, so once congestion reaches a critical point, energy must eventually return to the opposite side of this structure, where positive or negative energy flows in the same dimensional orientation.
This creates stable external North-South electrostatic and East-West magnetic energy orbits. For clarity I have shown this only in the electrostatic plane, in Figure 4 .
With the North-South and East-West flow of energy, electrostatic and magnetic poles develop; hence I’ve christened these structures ‘quantum poles.’ Refer to Figure 5 Spatial dimensions are compressed towards the temporal axis by external compression of electromagnetic orbits
Note the stronger e and m orbits do not encompass the spatial dimensions, they cut across them compressing them side on. It could equally be that they are engulphed by the spatial dimensions. Either works for what is to follow, as in the latter case, concentric orbital forces would also act to compress spatial dimensions onto the temporal plane from within.
If we compress quantum poles, either due to a large concentration of mass (and the resultant concentric pull towards the dimensionless point) or compression created by the exponential growth of reciprocal forces at the end of inflation. Spatial dimensions must then be compressed towards a common or ‘temporal’ axis shown East-West. When we discuss the nature of time, we will later postulate that this is actually the cause-and-effect basis of Einstein’s general relativity.
10 Propagation and Inflation
Let’s turn our attention to our familiar spatial dimensions once more. Again, I believe that orbital congestion will eventually force return orbits outside of the quantum structure, however these energy flows cannot form stable external orbits, as e and m orbits do. Here the opposing orbits are positive and negative energy and are therefore dimensionally offset, although they share the same plane. External energy flows would bring positive and negative energy together. However, being dimensionally offset they can never meet, though drawn to do so. They approach outside of the quantum pole, in dimensionless nothingness. Conditions again identical to the first quantum fluctuation. As energy flows are instantaneous at this point, we now have the conditions for infinite propagation or inflation. Inflation that now creates exponential reciprocal forces, ending inflation with an infinite universe, but under massive compression. Propagation and alignment of such energy structures in multiple dimensions gives us the basis for how our spatial and electromagnetic dimensions are created. Particle orbits will, I believe be too small and localized to align into overall dimensional fields.
11 A question of time
Massive compression of spacetime also provides, in my opinion, the only credible answer to the question that set me off on this quest for a new big bang in the first place:
“The moment you started reading this article was real, it happened, giving rise to cause and effect, as evidenced by the memories now encrypted in the neurons of your brain. It arrived rapidly, then in an instant and was gone. Anything with movement has energy. Everything real and all energy was created or released in the big bang, so where has that moment and its energy been for the last 13.8 billion years?” [2]
If the big bang happened everywhere, it didn’t have far to travel either, yet time is fleeting. It moves so fast that you can subdivide every second into billionths, using an atomic clock. I would argue that the only logical answer is time dilation. Einstein’s theory of general relativity [6] predicts the slowing of time under extreme gravitational compression. Within a black hole, the effect is so severe, that time approaches zero. Matter which fell into a black hole billions of years ago, to us as remote observers, still travels to its core today. Its gravity still affecting the stars around it [14].
So, what is time? Incredibly, for such an integral part of our existence, we just don’t know or can’t agree. A measure, a vector, a property of spacetime are common answers, but measures and vectors are not real things, they do not have movement. Universal properties are not unique, unlike the memories of when you first started reading this article. General relativity suggests that time might be a function of the compression of spatial dimensions and that severe compression causes time dilation. Time is also dynamic, for cause in one moment, to result in effect in the next, there must also be movement everywhere. Movement requires energy. Einstein’s theory of special relativity [3], demonstrated that time is also distorted by motion. So, time is likely a function of motion too. Coincidentally, we have universal motion; our universe expands everywhere and has always done so, since the first moment of existence [14].
12 Time Dilated Spacetime Energy Release
These highlighted observations are the basis for a new hypothesis; Time Dilated Spacetime Energy Release or TSDER [2], [7]. TDSER proposes a new definition of time. If true, it suggests highly plausible and consistent explanations for dark energy and dark matter. A missing piece of the cosmic jigsaw which joins together many others. The key points are summarized rather brutally below. It helps to have an overview, before we delve into each aspect in more detail. You have already met a few of these:
2. What we experience as time, is actually the rapid dynamic, time dilated decompression and/or propagation of these spacetime moments. This creates continuous movement in the temporal plane, transitioning to expansion in all spatial dimensions, enabling cause in one moment and set of spacetime coordinates, to move to effect in the next moment of release, everywhere.
3. Once expanded that moment has passed and spacetime has expanded everywhere, at the exact moment we call ‘now’. Time dilation explains where each moment has been since the big bang.
4. This time dilated release and decompression is also the basis of dark energy; potential energy stored by the extreme compression at the end of inflation, is released continuously and explains continuous universal expansion.
5. The extent of decompression must be proportional to the local energy density present, being set by the density of spatial dimensional orbital forces pulling any energy back towards innumerable dimensionless points. Any decompression of TDSER therefore matches the localized compression of spatial dimensions by massive objects. As the rate of this decompression sets how we experience time. Time must run slower in regions of higher gravitational compression; coupled with gravity+, we now have a full cause-and-effect explanation for general relativity.
6. TDSER into an expanded and therefore less energy dense universe, explains the acceleration of this expansion, currently attributed to unexplained dark energy. The reciprocal dimensional force created by the spatial expansion and energy momentum change explains universal gravity.
7. There was a one-off hot big bang; expansion from this post inflation compression is driven by radiation pressure [14] and as we shall see later, the disruption and breakdown of gravity+; due to the dimensional chaos caused by the ripping apart of the energy structures comprising spacetime, to create matter and radiation. This dimensional chaos creates an ‘advent horizon,’ releasing radiation pressure, like ‘popping a cork’ on spacetime compression, ending spacetime decomposition. A one-way barrier is created, over which ongoing time dilated decompression and propagation of ‘cold’ spacetime moments, still continues to this day.
8. TDSER creates movement everywhere, synchronized by the uniform conditions of compression and release everywhere, in a modified big bang. This continuous release of each moment starts along the temporal axis, then as spatial dimensions return to their natural orientation, decompression expands through all spatial dimensions equally; a continuous dimensional energy conveyor belt, allowing cause in one moment of spacetime release to move to effect in the next, everywhere.
9. The gravitational pull from the energy of unreleased TDSER moments, compressed invisibly along a temporal axis, into what I refer to as ‘subspace’, explains dark matter. Spacetime moments released over the advent horizon have no associated subspace or dark matter component, explaining the voids between gravitationally bound strands of dark matter . These increasingly isolated stands of dark matter create the macro structure of our universe, where a localized increase in gravity permits stars and galaxies to form.
13 Time and Spacetime Expansion
Okay, that’s a lot there to get your head around! So, let’s recap and develop some of these themes further, starting with time. With TDSER, time is dynamic, it is something real and each moment is unique; it will never happen again. The constant time dilated release of compressed spacetime moments is what we experience as the passage of time. Time flows from one moment of release to the next. Once released, the universe has expanded in all spatial dimensions, at the moment we call ‘now,’ and that moment has passed. Each spacetime moment is fleeting. A continuous and essentially infinite stream of spacetime moments rapidly decompresses, creating a conveyor belt of movement in all spatial dimensions. Cause in one moment of release, can therefore move to effect in the next across the entire universe. The arrow of time is set by the irreversible release and expansion of spacetime from subspace. We move only forward in time. Compression of spacetime due to accumulations of matter and gravity+ only slows the rate of release. It never moves backwards. The vector of time points along the temporal axis at the moment of release, then transitions and slows, as it expands fully into familiar spatial dimensions. There is uniform expansion of the universe everywhere (excepting slower local expansion around dark matter and mass accumulations), delivering the straight-line expansion described by Hubble’s law [1,14].
14 Relativistic Mass and The Speed of Light
Before we delve into time and special relativity, we need to discuss the speed of light in a TDSER universe. Newton’s first law [4], says an object with mass (a form of energy) travels at constant speed, unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Photons and other particles without mass travel at the speed of light. Yet those with mass can attain any velocity up to the speed of light, but can never attain the speed of light [3]. Particles with mass exhibit what’s known as relativistic behaviour. As they approach the speed of light, increasing amounts of energy are required, to accelerate them further. Much more energy than conventional calculations predict for the amount of kinetic energy, required to accelerate them towards the speed of light. In fact, to achieve the speed of light, infinite energy would be required. We can prove this both mathematically and experimentally, but why is this so? What fundamental forces govern this behaviour? Does relativistic behaviour, as it’s known, make sense in terms of the model proposed?
Firstly, let’s consider a particle with mass, within a TDSER universe. Again, for simplicity take a single spatial dimension, x. With TDSER we have a reciprocal force gxwhich acts on any energy in the same dimensional plane, so it acts on any particle with mass. In this model, this reciprocal force gx, limits the acceleration driven by the expansion of TDSER, to an equilibrium velocity, according to Newton’s first law. TDSER proposes that the velocity attained is the speed of light, i.e., TDSER is non-relativistic and I will justify that assertion shortly. Now, if we exert a force on our particle in expanded spacetime, it will start to accelerate. A change in the energy momentum of energy in the particle’s x orbit, so an additional reciprocal force must apply; the inertia of the particle, call this force gp. The particle’s spatial orbital energy is now subject to the combined reciprocal forces gx and gp. With gx being enough to limit a spatial orbits movement to the speed of light, even under the most extreme force; decompression from subspace. The inertial force, gp is also proportionate to the force applied to the particle. No matter how much energy or force is applied, the particle can never accelerate up to or beyond the speed of light. This gives us a basis for relativistic behaviour for particles with mass. Note that energy in TDSER orbits is not relativistic. It has only the reciprocal force gx, so may attain the speed of light. On this basis, any particles without spatial dimensions are therefore non-relativistic. A photon has no mass, any reciprocal force in the electrostatic or magnetic dimensions within which, its orbits surely reside, is at right angles to its movement through spatial dimensions. A photon on achieving the speed of light is not slowed on its path through spatial dimensions. It cannot move any faster, as that would move it into a previous TDSER moment, not yet released. It cannot travel back in time. Light can be deflected, by interaction with other orbits, but its velocity through spatial dimensions never changes unless the density of electromagnetic energy it enters changes. If light enters more compressed spacetime or matter, the increased electromagnetic fields created by gravity or the density of the media will slow or deflect light from its path. The constant speed attained is the same speed as any energy or radiation without mass can attain in an established spacetime universe, where such dimensional reciprocal forces are established by TDSER. We now also have a cause-and-effect basis for the constant speed of light.
So, if TDSER is not subject to relativistic concerns, we can treat each moment of TDSER on a non-relativistic or Newtonian basis. Each moment of TDSER released from subspace therefore accelerates until an equilibrium of forces is achieved in any spatial plane, TDSER reaches a fixed maximum velocity. A maximum speed which any energy in our spatial dimensions is limited to; being regulated by the combined effects of all dimensional reciprocal forces. TDSER asserts that this is the speed of light.
There is a constant flow of such moments, accelerating to a maximum constant velocity in the temporal plane, before moving into spatial axes and slowing as they fully decompress and have to push into full spatial planes. Each moment of spacetime released then being moved on as part of the constant release and expansion of subsequent moments. Each moment is fleeting, being delivered along the temporal plane at the speed of light. A universal time-dilated clock ticks at a constant speed everywhere, unless affected by the energy density of the local universe. Einstein’s curvature of static (previously released) spacetime by mass, is matched at every point of its curve by the dynamic expansion of TDSER to that energy density. As both are subject to the same forces of gravity+ set by the local energy density of the universe.
A cosmic clock, synchronized by the uniform conditions of the hot big bang, beats across the entire universe. You could set your watch by it!
15 Special Relativity
Within this TDSER universe, the weird effects of special relativity [3]; time passing slower when you’re in motion, now become intuitive. Travel in any direction, reduces the relative speed that TDSER moments can catch up with a traveller, when compared to a stationary observer. In simple terms, if you are moving in any direction, fewer moments of TDSER spacetime catch you up in that direction, compared to a stationary observer. Time therefore runs slower, the faster you travel. The effect is only significant when you approach the maximum speed of TDSER release. A constant stream of TDSER moments, each attain the maximum equilibrium velocity; the speed of light, in the temporal plane. So, the effect is only significant when the traveller is receding away from new TDSER moments at approaching the speed of light. When a photon moves at the speed of light, no new moments of TDSER can catch it. Photons do not experience time as we know it [14], but cause still follows effect and their environment feels the effects of time. TDSER provides a cause-and-effect explanation for special relativity. TDSER provides a compelling and indeed, in my opinion, perfect fit with how we experience time overall. No other explanation of time comes close. Special relativity also predicts that the length of an object must contract in the direction of travel, as it approaches the speed of light. Again, with mass composed of energy orbits, moving through an existing universe, the maximum rate of travel of energy is fixed to the speed of light. So, if you accelerate these orbits towards the speed of light, their orbital energy in the direction of travel can only attain the speed of light, hence length must reduce in the direction of travel.
16 The cold big bang
In the modified TDSER big bang proposed, not all spacetime was destroyed in the hot big bang. Inflation, the expansion and propagation of our energy structure has not stopped. Why would it? It must however now be slowed to a pace moderated by the reciprocal or gravitational dimensional forces it creates within an established universe. The speed of light. Infinite layers of compressed spatial dimensions or moments are then released (over billions of years to us, as observers in previously released spacetime), along a temporal axis. This answers the question of where each moment has been since the big bang. Each spacetime moment is compressed in a time dilated ‘subspace layer’ and hidden from our spatial reality, being aligned along a temporal axis. The opposite effect to matter and spacetime, drawn into a black hole billions of years ago, which from our perspective outside, still travels invisibly to its core, yet still affects us only through its gravity [2,14].
17 Dark Energy and Expansion
Once fully decompressed, the fleeting moment we call ‘now’ has passed and space has expanded, without dilution of its properties. A clear flaw with the current expansion model attributed to unexplained dark energy. Not to mention that if dark energy is needed to expand space in the conventional model, energy must also therefore be required to compress it. Dark energy, unless released along an offset temporal axis in proportion to its energy density, i.e., TDSER, would therefore act against such compression, slowing the earth’s orbit and dropping us into the sun!
If you prefer, the potential energy released by decompressing TDSER, is what we call dark energy. Expansion of spacetime in proportion to its energy density, into an increasingly larger and therefore more dilute universe, explains the current acceleration of this expansion. A tipping point is a logical outcome of TDSER; a time must be reached where gravity can no longer slow the expansion of spacetime into an increasingly less energy dense universe. The energy for universal expansion and conditions for new spacetime creation are attributable to the conditions present in the big bang. The only conditions we know of, capable of creating spacetime. Where are the extreme conditions necessary for spacetime creation in the fully cooled voids of space with the current model of the universe?
18 Dark Matter
TDSER says spacetime is energy. Highly compressed spacetime, yet to be released, locked away along the 4th temporal axis, must therefore affect the gravity of our universe everywhere, in the same way that a black hole affects nearby stars. Compressible spacetime, including this subspace layer, is at least a significant proportion of what we call dark matter. Present everywhere (initially anyway) since creation, compressed around massive objects and interacting weakly only through its gravity with matter [8]. This subspace can be envisaged as an underlay to Einstein’s spacetime fabric. However, with ongoing TDSER, each new moment of spacetime released also creates new spacetime, but crucially, spacetime without this subspace layer.
TDSER produces spacetime voids, space devoid of dark matter. It is the voids between galaxies which are expanding in our universe [8]. The new spacetime released, we know interacts very weakly with matter in our universe, we frequently refer to the vacuum of space. TDSER would act only very weakly on matter and spacetime with a dark matter substrate. Gravity will hold dark matter accumulations together. This new spacetime will logically therefore expand and create expanding voids in the space between dark matter accumulations. Mapping of the structure of dark matter in our universe suggests that it is concentrated into a 3-dimensional invisible lattice of an unimaginable scale. Galaxies and stars are formed along these dark matter strands and particularly at junctions where dark matter strands meet [8]. Once again, we have an excellent fit with observation. With this model of the universe, it must have been more energy dense in the past, so we would expect to see galaxy formation much earlier than the conventional big bang. Something that the JWST results appear to be confirming [15].
19 Gravity – Newton or Einstein?
Einstein’s gravity is often visualized, using a bowling ball on an elastic sheet, to show how mass compresses and distorts the fabric of spacetime. Einstein said that no force acts on the ball or earth, it moves in straight lines through a landscape of curved spacetime, but did not explain why matter curved and compressed spacetime.
Newton explained gravity as a force created by mass, like the earth. His equations work in almost every circumstance and perfectly for describing the interaction between force and mass, but are not as accurate in cases of extreme gravity [4,6]. How can both of these very different and respected models be correct?
Let’s consider gravity in a TDSER universe, refer to Figure 6. A force; a reciprocal dimensional force, caused by the ongoing expansion of TDSER spacetime energy, acts on the concentrated energy of the ball and the earth, but also on the energy in our spacetime-subspace fabric compressed through the effect of gravity+. Gravity+ acts to compress and distort spacetime towards innumerable dimensionless points, back along the temporal plane. With TDSER, the ball and subspace fabric can never meet, that would involve time travel.
TDSER creates a balancing force from the fast release and decompression of initially very compressed spacetime along the 4th dimension. The strength of the balancing reciprocal force created, is set by the mass of the ball, because the density of spacetime released, is also set by the local mass energy density of spacetime, into which it is released. The net force acting on the ball equilibrates to zero, no matter how large the mass of the ball. A bigger ball simply sits in a deeper ‘depression’ of more concentrated energy, matched by the higher decompressive potential energy of TDSER at that point in spacetime. See Figure 6 Gravity according to TDSER
Newton’s gravitational force (our reciprocal dimensional force due to TDSER) acts on the ball and gravity+ acts on the spacetime-subspace fabric, their combined energy causes compression and distortion of subspace, allowing the ball to move in a straight line, with no net force acting on it, through curved spacetime, just as Einstein said. With TDSER, both models are reconciled.
Hence the predictions of Newton’s and Einstein’s equations are very similar, but not identical. Newton’s equations are based solely on the mass of the ball, whilst Einstein’s predictions are based on all the energy present, in which Einstein included what he called the energy of gravity [6]. With TDSER the spacetime-subspace fabric is energy and is also distorted by gravity+. This is the ‘energy of gravity’ Einstein introduced into his equations to match observation, so Einstein’s equations correctly predict Mercury’s orbit, but Newton’s do not. Mercury’s orbit is close to the sun. Gravitational compression of the spacetime-subspace layer is significant enough to affect its orbit.
20 Charge and the Hot big bang
I stated earlier, that the violent deceleration created by exponential growth of reciprocal dimensional forces during inflation, provides the perfect catalyst to initiate the hot big bang; creating the exponential compression of all of the energy released in inflation, everywhere. Spacetime structures, under such conditions might logically become merged into more energy dense forms or ripped apart, releasing free energy orbits as particles or radiation. Logical enough, but I am seeking to explain this modified big bang on a cause-and-effect basis, so how this might occur?
What follows is speculative. An illustration of how such events might have occurred. I offer it as a ‘straw model’ for debate and discussion. It is however logical and again potentially offers an alternative view as to how the early universe may have developed during the modified big bang proposed. In particular, the definition of charge I will suggest, offers a potential answer to the perplexing problem of anti-matter asymmetry.
Under massive compression, orbits within quantum poles must be pushed closer and closer together, causing deflections and eventually twisting. The electrostatic orbits will be twisted by a greater and greater extent, driven by the asymmetric deflections from strong particle orbits, compared with deflections produced by much weaker spatial orbits. Refer to Figure 7 below. The orientation of this electrostatic twist, relative to the fixed background electromagnetic field, depends on whether the orbit resides in the upper or lower hemisphere of the quantum pole. This I believe is an excellent candidate for the property we call charge. Energy is potentially locked into this twist, by the parallel compression of its negative energy or force pair, stabilizing the charge in proportion to the extent of compression. See Figure 7 Development of charge within a quantum pole under extreme compression.
If we call the deflection in the top hemisphere a negative charge and that in the lower hemisphere a positive charge. Bring 2 charged particles close enough to interact, then there will be a release of these twists of potential energy and 2 neutral particles result. Bring an electron and its positively charged anti-matter equivalent together, the dislike charges attract. The result is 2 neutral photons with high energy. How and why, they must attract in this model will be explained in the later section on force carrying messenger particles. Similar deflections may also take place on magnetic orbits, perhaps imparting the basis for the property of angular momentum called spin?
The spatial orbits will also be affected, twisting of the electrostatic and magnetic orbits must therefore create an asymmetry within spatial orbits. In our universe, spatial orbits are deflected and align preferentially towards the lower positively electrostatically charged hemisphere.
This asymmetry bringing spatial orbits preferentially closer to positively charged electrostatic orbits at the commencement of the hot big bang, is potentially the reason our universe exists at all, the basis behind matter / anti matter asymmetry [12]; why there are more positively charged matter particles in our universe (explained later in greater detail, if you are unfamiliar). This twisting also provides us with something else crucial for the hot big bang. Stress or fracture points within quantum poles. Compress them too far and they must eventually twist themselves apart. As spacetime as a whole is massively compressed, towards the end of inflation, orbital compression and strength builds. Simple geometry suggests that with extreme compression the weakest spatial dimensions would be pushed inside the electrostatic and magnetic orbits. Spatial orbits will become flattened towards a common plane, the temporal axis by the pull on all energy towards the common centre of overlapping orbits described earlier. Refer to Figure8 below.
The electrostatic and magnetic orbits in turn will also be pushed towards and overlap the orbits closest to rift. In this model, the orbits closest to the rift will provide the framework within which particles and the familiar atomic structure can develop. See Figure 8 Compressive forces push dimensional forces inside particle orbits
There may be many of these micro dimensions, each imparting different properties to the particles they will give rise to. I will describe a model where fragments are pushed within dissimilar particle orbits. Another option is that fragments simply combine under extreme energy and compression, similar orbits push into each other, akin to ‘push shuffling’ a deck of cards; like orbits are pushed together, sharing a dimensionless point and adding to the strength of all shared concentric orbits, or perhaps there is a combination of both.
21 The Hot Big bang and matter anti-matter asymmetry
Again, I would regard this section as illustrative. I have no evidence for what I will propose, it just makes more sense to me this way and aligns with the observed structure of matter in our universe. Simultaneously, charge is developing and tensions within quantum poles reach breaking point, shattering quantum poles into fragments along the stress points created by charge; the twisting of electromagnetic orbits. The result: spatial dimensional orbits, pushed towards the positively charged electrostatic orbits in the lower hemisphere, preferentially combine with electrostatic and magnetic orbits from that hemisphere. See Figure 9 The Russian doll of concentric particle orbits
Further decay, combination and confinement could then give rise to the standard model of particles, with positively charged mass bearing particles preferentially confined within the strongest inner concentric orbits, like a Russian doll, as quarks see Figure 9. The building blocks of protons and neutrons. Notice, I have not mentioned the force carrying particles of the strong force, the gluon and meson [1,11], in this simplified description. We will return to explain their creation in a later section on forces and messenger particles. Fragments with spatial orbits occupy 3-dimensional space and have reciprocal inertial / gravitational forces i.e., they have mass. Any spatial dimensions combining with a negative charge to form anti-matter will be rapidly ‘annihilated’ or rather interact to neutralize their charges. The potential energy stored, released as high energy radiation in a sea of photons and other particle combinations.
As there is a preferential alignment of spatial orbits to form positively charged particles, we have no anti-matter in the universe, except when we manufacture it. Current theory provides no explanation why we have a matter universe. Under laboratory conditions, whenever we create matter, it comes with an oppositely charged anti-matter twin and the two rapidly annihilate each other in a shower of high energy photons and / or other particles. The conditions of massive compression are simply not present under laboratory conditions. There may be enough energy, but no exponential gravity+ compression to create the charge asymmetry and hence preferential attraction needed.
In the illustration above, I have suggested that some of the electrostatic and magnetic orbits are moving around the whole quantum pole. These ‘free’ orbits may or may not attach. That would be a matter of probability. My best and simplest guess is a that there are 3 electrostatic orbits, 2 of which are free. Quarks are endowed with a charge of +/- 1/3 or +/-2/3 dependent on whether they have 1 or 2 free energy orbits of a positive or negative orientation or charge.
The next layer out in these ‘Russian doll’ particle orbits provides a home for confining protons and neutrons together into an atomic nucleus. Some expansion and therefore cooling may be necessary, before this can happen, but the Russian doll of nuclear forces has already been formed. Forces in the current models of the big bang are currently believed to separate from an unknown fundamental unified force and establish with cooling [13]. With this model, extreme compression provides enough energy to confine similarly charged particles together. Their combination within these force energy shells only tightening their grip, compressing orbits in orbits, concentrating concentric forces, crushing them further towards their respective dimensionless points.
Free charged electrostatic and magnetic orbits would logically combine to form leptons. There will be an excess of negative charge available, as spatial particles have locked away most of the positive charge. The most familiar, the electron may have 3 electromagnetic orbits, imparting a charge of – 1. The outer orbits of this Russian doll are good candidates to create shells in which electrons can be captured. Drawn towards the oppositely charged nucleus, but destined never to collide; being dimensionally offset from this protective particle dimensional shell due to their electromagnetic dimensional alignment. Electrons will therefore orbit the nucleus. As the universe expands and cools, or within stars formed millennia after the big bang, these protons or hydrogen nuclei can combine to form helium, adding another proton, but also combining energy shells for electrons.
There may be any number of particle orbits within a quantum pole. I have chosen to represent them according to the charge combinations possible in Figure 10. The charge combinations can then be shown to match the standard model of particles [2].
The ripping apart of spacetime under extreme compression and innumerable matter anti-matter ‘annihilations’ gives rise to a sea of high energy photons and other particles and must create chaos. In this chaos, the dimensional alignment of particles, radiation and quantum poles must surely break down. This alignment is the basis for the force we called gravity+. The synchronized breakdown of gravity+ coupled with extreme radiation pressure from the photons and other particles created, initiates massive expansion everywhere, simultaneously. This creates the advent horizon, releasing the compressive forces, ending the destruction of spacetime and leaving behind a super-compressed time dilated subspace we call dark matter.
I may well be off the mark with some aspects of the surely simplified model presented, however my aim was to demonstrate that TDSER and balanced energy-force orbits can deliver a logical consistent and credible cause-and-effect big bang. I believe, it has delivered on that, but also potentially provides a credible potential solution to the puzzle of anti-matter asymmetry. See Figure 10 Potential charges within particle orbits
22 E=mc2
This one will be highly contentious. There is another logical consequence of TDSER, spacetime, having spatial orbits and reciprocal forces, must also have mass. Not much, it must be very dilute, but it has non-relativistic mass in this model. As spatial orbits expand along the temporal plane and move into spatial planes, they are subject to reciprocal forces due to their energy movement away from the dimensionless point on every part of their journey. They will rapidly attain the maximum constant equilibrium speed, the speed of light (being non-relativistic). A continuous stream of spacetime moments is released and reach the speed of light. Then, as they expand into spatial dimensions, they must effectively push their way into full spatial dimensions, creating movement and expansion in those dimensions. They impart all this energy and eventually come to rest at an equilibrium size, matching the local energy density of the universe they have pushed into. This provides the dark energy needed to expand our universe.
Any mass, within our universe, having 3 spatial dimensional orbits and corresponding reciprocal forces which travels through spacetime at a velocity v along a particular trajectory, possesses what we call kinetic energy, e. The amount of kinetic energy for mass, at low non-relativistic velocities, and hence non-relativistic spacetime, being composed of the same energy, is therefore given by equation 3:
e = ½ m v2 (3)
TDSER attains the speed of light in the temporal plane, but then slows as it expands, imparting all of its kinetic energy to its surroundings. Like inflating a balloon in a ball pit, pushing apart spacetime. Eventually spacetime expansion slows to zero, fully transferring all of its energy, at the moment we call now. The energy transferred to its surroundings is therefore that of non-relativistic mass moving at the speed of light. However, if we remember the earlier discussion on dimensional planes; orbits have shared dimensions (length and breadth, breadth and depth or length and depth) and therefore their expansion takes place in 2 planes. So, the kinetic energy imparted is simply twice that given by equation 3, or once again equation 1:
e = mc2 (1)
This is therefore also the energy required to compress spacetime to the size it was, when it could be confined within other energy-force orbits, into particles. Although our mass of spacetime was not confined, its energy must be the same as that which was achieved in subspace, when a proportion of our universe was. A compression equivalent to that needed to form matter particles.
Hence if you released these spatial fragments confined within matter particles, you would release the same amount of kinetic energy. Equation 1 therefore tells you how much kinetic energy is released, either from decompression from subspace or in nuclear reactions, where matter is released from confinement. I differ from Einstein’s interpretation here, the mass is not destroyed in nuclear reactions, it is released from confinement by the nuclear forces created during the hot big bang, releasing its kinetic energy and the ‘missing mass’ released has expanded into spacetime. It is no longer a particle, what is left joins the fabric of spacetime. If we had destroyed any of these balanced positive and negative energy paired orbits, the sum of the energy released would be zero. This also means that stars are in effect creating additional spacetime, adding to universal expansion, beyond normal TDSER. A component of their solar wind, which we might be able to quantify?
23 Force carrying messenger particles
I claimed earlier that this simple model could potentially create all of our fundamental forces. The following justification of this rather bold statement will, I believe, further highlight the potential power of this model; by bringing of all things, common sense and cause-and-effect to the quantum world. I claim no expertise in this area. I will give only the most basic explanation of such interactions, so as to demonstrate a consistent and common approach, which I believe is most likely responsible for such forces. I accept that I may be some way off the mark with these, but again there is, I believe great potential to develop this model much further.
Conventionally, all forces are carried by messenger particles or at least perturbations in background fields which can be modelled as virtual particles [1,11]. I do not doubt or contest the mathematics behind these theories; however, I believe that this model can explain the true nature of such virtual particles. I’ll start with the electromagnetic force.
23.1 The Electromagnetic Force
The conventional view of forces is that they are conveyed by carrier or messenger particles. Photons or so-called virtual photons, which quantum theory says appear from nowhere and exist only for a very short time, are the recognized messenger particles of the electromagnetic force. Charged particles repel each other by exchanging virtual photons. We are told to imagine two baseball pitchers in space, the force of throwing the ball and of receiving it, pushes each of them apart. Examples I have seen to date, conveniently gloss over attraction, which is considerably less easy to explain with this analogy. Messenger particles must be released in all directions continuously as they can hardly detect the presence of another charged particle. How, why and where the energy comes from to create what must be an infinite number of these messenger particles is not understood.
Only those messenger particles that successfully find a target, transfer any energy (again unexplained), the others simply disappear. If the particles in question move at light speed, there is a further problem. Virtual particles are then moving through spacetime at beyond the speed of light! Also, what holds the energy in messenger particle together? Don’t we need a force? It’s all very odd indeed, but the quantum world is strange, or so we’re told. However, if you accept that everything in our universe, including matter and spacetime dimensions, are composed of balanced energy-force orbits. This behaviour actually makes perfect sense, just not as described above.
Let’s take the property we have been looking at; charge. There is a force that brings together oppositely charged particles or repels similarly charged particles. The property of charge we have suggested will be formed under extreme compression and we have further proposed how this compression twists and locks in potential energy in charged particles, relative to the electrostatic plane. Positively and negatively charged particles therefore have the opposite orientation to the electrostatic plane. As such they must deflect background dimensional orbits in opposite orientations (even if you doubt my earlier explanation of charge).
With TDSER we also have continuous release and expansion of spacetime orbits in all dimensions (an energy source to provide movement everywhere). As TDSER is released or moves, it will align dimensionally or be deflected by the background dimensions or any other orbits in the same plane. It will also expand to match the local energy concentration present. The presence of matter or a particle will therefore increase local energy concentrations centered upon that matter or particle. There will be countless interactions and deflections. A recipe for absolute chaos? Maybe so. The outcome of innumerable interactions can only really be determined by probability, as a result. However, if we apply some relatively simple principles, perhaps we can see through this fog of confusion.
Another definition, of force carrying messenger particles, is that they exist as quantum units of excitation in an electromagnetic field. Points of increased energy above a baseline level [11]. Note, this definition actually implies energy is present in electrostatic and magnetic planes. If such energy exists as orbits, stable electrostatic and magnetic force orbits must also exist in these planes. Electrostatic and magnetic forces are always offset by 90 degrees and create an overall electromagnetic field.
Okay, let’s throw in a charged particle. Ignore for now the effect of TDSER. If the charged particle is in motion, and they all are. There must be interaction between the charged particle’s electrostatic orbits with those of the background electrostatic dimensional energy orbits. Orbits in the direction of motion will be deflected by the oncoming particle. The particle’s energy orbits are full, so they cannot combine, even when they share the same dimension. The result is compression of background energy orbits around the particle in that plane. An elevated level of electromagnetic energy, centred on the particle, but extending beyond it. Note if the particle cuts the background dimension’s orbital path, which then deflects the background orbit in front or behind it. It does not draw any energy from the particle to do so. Now let’s add in TDSER. See Figure 11 below, the particle is depicted by 3 red concentric energy orbits in the electrostatic plane. There will also be more orbits in other dimensional planes. See Figure 11 Particle with electrostatic orbits passing through background dimensional energy orbits and TDSER
There was already an elevated concentration of energy centred on the particle, but if we add in the effect of TDSER, we add further concentric orbits. There is an elevated energy density even compared to other TDSER energy, because TDSER matches the local energy density. An elevated concentration of energy is now centered on our particle, but is in constant motion and extends well beyond it. These concentrations of energy orbits now move through the background electrostatic field, like waves centered on the charged particle. Note that I have shown the source of TDSER centered on the particle. It could equally be offset, but the localized concentration of energy would still be similar. As electrostatic and magnetic dimensions are offset at 90 degrees, such interactions must also cause similar deflections in magnetic dimensional orbits. There will be magnetic energy concentration centered on the particle too.
Crucially, positively and negatively charged particles being oppositely twisted and oriented within the electrostatic dimension will also create opposing deflections of the background electrostatic orbits, out of the electrostatic plane. As TDSER is released it must also align or be deflected in a characteristic manner with this twisted background. If negative charges create a deflection to the south, as shown in the side on view below, then positively charged particles create a deflection to the north. These orientations effectively create opposite elevated energy peaks. We now have an energy landscape in the electrostatic dimensional plane.
When two negative particles come sufficiently close, energy peaks of the same orientation overlap, adding like wave crests, creating a larger deflection. Both charged particles are deflected, pushed ‘downhill’ acquiring energy in the opposite direction to the point of ‘contact’ driven by the movement and expansion constantly created in all directions by TDSER. Negative charged particles therefore repel each other. Notice, we now have peaks of electrostatic and magnetic energy, dissipating outwards, centred and concentrated around the charged particles. Spikes of energy now exist as quantum units of excitation in an electromagnetic field. Matching the earlier bolded definition of a virtual particle. TDSER provides an energy source to drive movement and interaction through these energy peaks. I will now refer to these peaks as virtual photons. See Figure 12 Side view of negatively charged particle relative to the electrostatic plane.
These virtual messenger particles are now created due to cause-and-effect, they are not emitted from the charged particle. They are deflections in the orbits of dimensional energy or TDSER. So, don’t require particles to break the speed of light through spacetime. Remember, movement within orbital planes are not subject to reciprocal forces and are therefore not limited to the speed of light. You can also argue that electrostatic and magnetic planes being at right angles to the temporal plane feel no effect of time and can in fact move at infinite speed.
Other virtual photons, peaks which do not make ‘contact’ will dissipate without energy transfer, as their orbits return to their original path, as the particle moves on. Orbits which are once again dependent only on their momentum and interaction with their negative energy equivalent. Positively charged particles cause distortions facing west, again positive particles also repel.
Dislike charges also create virtual photons, but with opposite orientations which will effectively cancel. No hill between these particles, but there are moving hills albeit of opposite orientations now pushing on the particles due to TDSER expansion from every other orientation in that dimension. Like a pair of lazy hikers descending into a valley from opposite sides, they are drawn together. Dislike charges attract or if you describe it as Einstein did for gravity, the particles move in straight lines through a warped electromagnetic landscape. One warped both by energy concentration and in this case charge. Cause-and-effect and dare I suggest common sense in the quantum world! Whatever next?
This creates a simple, opposing peak rule for electromagnetic interactions, which mirrors that seen in other wave forms. Dislike charges create virtual photons, concentrated deflections in the electromagnetic field with opposite orientations. TDSER creates movement of these virtual photons, ensuring that dislike deflections cancel, causing attraction whereas like deflections repel. Both transfer energy in the direction of contact. Reference [2] uses this rule to propose how Ampere’s right-hand rule and attraction or repulsion between parallel wires carrying electricity would also match with observed behaviour in such a universe.
When pointing out the synergies between string theory and balanced force-energy orbits earlier, I stated that strings are energy loops that vibrate at different characteristic frequencies, which are attributed to different properties, like charge or mass. In the interactions we have seen, energy orbits will have a fixed size and tension depending on the background local energy, their own energy or how they are confined. They will also have electromagnetic orientations set by their charge and will therefore cause different characteristic deflections in background electromagnetic and presumably also spatial dimensions. In this model such energy loops must therefore themselves adopt different characteristic frequencies, as a result of their charge and these interactions. The result is the same, characteristic vibrations of energy loops, but that I believe is an effect, not the cause of charge and mass, which we have already partially defined within a TDSER universe.
23.2 Force carriers for the Strong Nuclear Force
The strong nuclear force, in conventional particle physics, acts over two ranges. Over short ranges (less than the size of a nucleon) it has a force carrier called the gluon, reputedly responsible for gluing together quarks within a proton or neutron. The quarks themselves appear to change their property of ‘colour’ with each interaction. Gluons themselves have no mass, but rather strangely, the mass of a proton or neutron is much more than the sum of its constituent parts [9].
This new model might suggest a different interpretation, although again I would regard this as illustrative. We already have a strong Russian doll of nuclear forces within which to confine quarks and also nucleons within an atomic nucleus. We also have the compressive forces required, with the compressive reciprocal forces that end inflation and instigate the hot big bang. In the model proposed, within a proton or neutron, tightly bound quarks will have multiple very strong concentric spatial orbits which, in such intimate proximity, must also deflect each other, causing wave patterns and interference, this time in 3 dimensions within nucleons. Peaks and troughs of spatial energy are created. Virtual particles, we see as gluons, are created which carry energy between the quarks, thus constantly changing their apparent properties or colour in the process. These deflections involve energy movement, but still within spatial dimensions. For example, an orbit with width and length will be deflected into depth. As such these deflections create a change in energy momentum in that dimension and therefore a reciprocal spatial force is created. These virtual gluons, being confined within matter will also therefore have relativistic mass. With numerous gluons for each quark, this mass will dominate, especially at high energy and a proton or neutron must have a much greater mass than its constituent parts.
The strong force also acts over a longer range and binds protons and neutrons together into a nucleus by exchanging mesons [9]. Protons and neutrons have mass and therefore spatial orbits from their constituent quarks. These orbits must again interact, undergoing internal deflections and creating interference patters. This model would suggest other virtual particles with mass would be created in a similar manner. Potential candidates for mesons.
23.2 The Weak Force
The above illustrative explanation of the strong force, you will note, has no role for TDSER. TDSER expansion will also be present and must interact with the chaos caused in all orbital dimensions, which quarks and the nucleons they create have dimensional orbits in. So, TDSER must interact with spatial dimensional orbits on this scale too, however the strength of unconfined TDSER orbits as they are released will be much weaker than those of confined particles. TDSER must also create virtual particles with spatial dimensions or mass. They will therefore transfer energy and therefore cause changes in the protons and neutrons they interact with. The weak nuclear force is a force carried by bosons. Particles with mass, which might again help to explain why a proton or neutron, appears to be more massive than the sum of its parts. Especially as a deflection on this scale, can easily be greater than the depth or breadth of a confined spatial orbit. The extent of these deflections must be proportional to the change in momentum of their energy and hence the reciprocal forces in spatial planes responsible for mass.
I believe that this at least illustrates the potential for such a model as is proposed to create the four ‘fundamental’ forces of nature; which takes part in nuclear reactions including fusion, fission and radioactive decay. The exact cause and effect mechanisms of those, I will leave for others. They are reportedly well understood. My intention here was simply to show that there is at least a consistent and potential fit, with all of the ‘fundamental’ forces of nature and their associated virtual particles. That a single unifying force, forged in the first instant of creation, has the potential to explain, in a consistent and logical manner, all the other ‘fundamental’ forces: gravity, electromagnetic, strong and weak nuclear forces.
23.3 The Higgs' field and mass
Conventional theory says that the Higgs' field is created by a carrier particle, the Higgs' boson. The Higgs' field, a field present throughout our universe, is believed to be responsible for giving particles their mass. The more a particle interacts with the Higgs' field, the higher its mass [9].
So how does this fit within our new model? In an established universe, we have spacetime dimensions everywhere, composed of innumerable energy orbits aligned on spatial axes, balanced by negative energy or force orbits. With TDSER and all particles with spatial dimensions creating interference patterns within the background dimensional orbits. Peaks and troughs or virtual particles with mass are created (I presume the Higgs' boson), which appear as phantoms, moving and disappearing with each moment of TDSER released. Any deflection in a spatial orbit with length and breadth, will cause a deflection or energy momentum change into the third spatial dimension depth. Thus, creating a reciprocal force. Particles with spatial orbits will therefore be cocooned in these inertial dimensional reciprocal forces in all spatial dimensions, increasing their mass. This I believe is the nature of the interaction of particles with the Higgs' field. A field of spatial dimensions we have already created everywhere, together with those of TDSER being released and bringing motion, time and cause and effect.
Particles with spatial dimensions will create localized deflections in all spatial orbits and therefore create mass around themselves, but the particle also has mass in-its-own-right too, due to its spatial orbits and the reciprocal force created by TDSER responsible for universal gravity. Again, the fit is good. The mathematics to describe the behaviour observed has not changed, simply the understanding of how it occurs. If strong particle deflections create the Higgs' boson, might we one day detect the interaction between TDSER and background spatial dimensions. Would this perhaps correspond to the properties we attribute to a graviton?
24 Electromagnetic radiation and wave particle duality
During the hot big bang, we created free electrostatic and electromagnetic orbits. Combining these into particles, with no spatial orbits, provides us with perfect candidates for electromagnetic radiation – with no mass, travelling at the speed of light and carving out offset electrical and magnetic wave patterns as they spin. They would have an apparent wavelength, amplitude and frequency; dependent upon their energy. Electrons and more famously neutral photons exhibit properties associated with both particles and waves. Fire photons through slits in a metal sheet and they will travel in a straight line and convey discrete packets of energy to a receiver on the other side. So therefore, photons are particles.
Narrow the slits and they then behave as waves; being diffracted through the slits to form wave fronts which then collide in interference patterns on the other side. So, a photon is also a wave! This is ‘wave particle’ duality – it is both [16]. Even a single photon will appear to interfere with itself when passing through a narrow slit. Very peculiar indeed!
With this new model, again this behaviour now makes perfect sense. If the slit is narrow enough, the ripples in the background electrostatic orbits caused by a photon (and TDSER) or other particle with electromagnetic orbits will interfere with similar electromagnetic orbits of the atoms in the wall. The real give away is that even a single photon will be deflected from its path when passing through a slit, in a similar way. With paired and offset electrostatic and magnetic orbits, wave particle duality also now makes complete sense. A single electron no longer apparently passes through both slits simultaneously to deflect its own path. It simply interacts with the orbits in the slit walls when brought close enough to do so. Otherwise, it passes through a wider slit, unaffected. Measuring the slight asymmetry in the pattern formed might prove this.
25 Spooky Interaction at a distance
Spooky interaction at a distance, or quantum entanglement, to give it a much more boring scientific name, is a very weird effect, seen on the smallest scales and now proven experimentally. So-called entangled particles, created or separated in a common event, appear to have undetermined properties, for example; their spin appears to be unresolved until ‘observed,’ when they suddenly decide, apparently at random, to adopt a particular property. Upon this observation, the other entangled particle will instantaneously take on the opposite property. This effect holds true, even if the particles are separated by immense distances. Farther than light can travel in the time available!
Einstein was famously not a fan of this effect, predicting its requirement mathematically, then presenting it as an anomaly in quantum theory, which meant that quantum theory wasn’t the full story [17]. A view, I hope you now share. It flies in the face of cause and effect, the deterministic nature of the universe; where one thing leads to another. But if we replace the word ‘observe’ with ‘interact’, then it begins to make sense in this rather less strange new universe, we have created.
Photons can be entangled by firing a laser at a crystal, splitting a photon it into 2 entangled photons. I am a determinist at heart, to me cause leads to effect. I strongly suspect that during interactions or splitting of particles, which result in entanglement, the resulting particles are indeed entangled in a very real sense. Observation at a very small scale involves interaction, as it requires some type of messenger particles to observe something, thereby affecting what you are observing. We rely on bouncing photons or other particles off something in order to detect it, thereby affecting what we are trying to detect.
In the universe I have been describing, we have created dimensions and particles with energy orbits in electrostatic and magnetic planes. These planes run perpendicular to the temporal dimension and independently of spatial dimensions. The possibility of instantaneous effects between particles, connected in some way through entangled energy orbits in the electrostatic or magnetic planes, yet separated within spacetime dimensions is therefore completely credible. Weird effects such as ‘Spooky interaction at a distance’ might actually be expected and logical outcomes in such a universe.
My thoughts on quantum entanglement are as follows. With entanglement of orbits in at least one non-spacetime dimension, two particles which at one time shared the same coordinates in spacetime, can still share a common energy orbit in non-spacetime dimensions, whilst moving away from each other through spatial dimensions. The interaction between electricity and magnetism is always at 90 degrees and entirely separate from any spatial movement we apply. So spatial movement in itself does not necessarily disturb or break electromagnetic orbits.
Entangled electrostatic or magnetic orbits, being orbits (and not stretched loops of energy) orientated perpendicular to the temporal dimension can interact instantaneously across infinite space. Such that when an interaction happens with one of the entangled particles orbits, it may reconcile to either one entangled particle or the other; perhaps gaining a magnetic orbit to push its spin from one state to another. The other reacts in an equal and opposite manner having lost its share of that orbit, ensuring that the balance of the universe is maintained. Which one it reconciles to will be completely random. Even spooky interaction at a distance, the strangest ‘magic’ of all, now makes sense on a cause-and-effect basis with the model proposed.
26 The TARDIS+ and Concluding Comments
Figure 13 is an attempt to summarize the TDSER universe in a single diagram. I have christened it the TARDIS+ in honour of my daughter Maya’s crush on a certain Doctor Who actor. TARDIS+ stands for ‘Time and Relative Dimensions in Spacetime+’. Based on a quantum pole in subspace, it is centred on a dimensionless point and shows dimensions in red on the LHS and forces on the RHS, in blue. Refer to Figure 13 The TARDIS+
Particle orbits are shown as solid circles, with their potential charge combinations around the perimeter. On the left, spatial dimensions x, y and z are compressed along a temporal axis, then released over an advent horizon, as TDSER or dark energy. This creates reciprocal dimensional gravitational/inertial forces shown in blue; gx, gy and gz everywhere. Electrostatic and magnetic planes are denoted s and r respectively, with corresponding reciprocal electrostatic e and magnetic m forces. These will be encompassed within our spatial dimensions, once they expand over the advent horizon. G+, the compression of spacetime due to concentric compressive forces of energy orbits is shown between the electrostatic and magnetic forces. I have also shown St and w for strong and weak nuclear forces created by our Russian doll of particle orbits. The bottom RHS, depicts the fundamental balanced energy-force orbits and the single unifying force towards reconciliation, which brings balance and stability to our universe, which I have christened rather hopefully as ‘peace.’
I cannot prove TDSER mathematically, nor a universe composed of balanced force-energy orbits, any more than Darwin could prove evolution in those terms. TDSER does not change our reality or mathematical models that describe it, rather it potentially explains why it exists that way. It suggests a common cause for the effects we take for granted; time, gravity and spacetime compression and possibly even our ‘fundamental’ forces. TDSER successfully describes our universe on every scale and provides a perfect fit with how we experience time, unexplained dark energy and dark matter. Balanced force-energy orbits have the potential to create stable dimensions, matter and radiation, and may also explain atomic structure and matter anti-matter asymmetry. We have a proposition for a single unifying force which provides cause-and-effect explanations for mass and inertia, wave-particle duality and even offers to bring sense to the weird and wonderful quantum world.
The ask is straightforward, to offer this new model up to a wider scientific audience. To have it scrutinized and debated. If this is indeed what happened in the first moment of creation, then just perhaps it has the potential to move physics out of a dark age of unexplained dark matter and dark energy, and into a new era of cause-and-effect.
References
[1] UK Essays. (November 2018). Standard Model of Cosmology: Overview and Analysis. https://www.ukessays.com/essays/sciences/standard-model-cosmology-overview-3437.php?vref=1
[2] McCoard M., (February 2024) Everything, 1st Edition, KDP amazon ASIN: B0CVW2C6F2,
[3] Einstein A. The Theory of Relativity, (1911); Manuscript on the Special Theory of Relativity, 1912
[4] Newton I. (1687); Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica.https://doi.org/10.5479/sil.52126.39088015628399
[5] Mohaupt, Thomas. (2022). A Short Introduction to String Theory.
10.1017/9781108611619.
https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108611619
[6] Einstein A. The basics of general relativity theory. Annals of Physics. 1916; 49:769-822
[7] McCoard M. How to fix the universe, (February 2023) KDP amazon, ASIN: B0BX285M3N,
[8] Katherine Garrett, Gintaras Duda, Dark Mater: A primer arXiv:1006.2483v2 [hep-ph] https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1006.2483
[9] Brookhaven National Laboratory. "Quark matter's connection with the Higgs: Heavy ion collisions delve deeper into the origin of (visible) mass." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 14 August 2012. <www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/08/120814121444.htm>
[10] Mary Gaillard, Paul Grannis, Frank Sciulli. The Standard Model of
Particle Physics
https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.71.S96
[11] Jaeger, Gregg (2019). "Are virtual particles less real?" (PDF). Entropy. 21 (2): https://doi:10.3390/e21020141
[12] Kolb, Edward; Turner, Michael, eds. (1988). The Early Universe. Frontiers in Physics. Vol. 70. Redwood City, CA: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-11604-5. LCCN 87037440. OCLC 488800074.
[13] Big Bang models back to Planck time". hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu. Retrieved 28 April 2020.
[14] Hawking, Stephen W. (1988). A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black Holes. Introduction by Carl Sagan; illustrations by Ron Miller. New York: Bantam Dell Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-553-10953-5. LCCN 87033333. OCLC 39256652.
[15] Citation: 'Beyond what's possible': New JWST observations unearth mysterious ancient galaxy (2024, February 14) retrieved 7 June 2025 from https://phys.org/news/2024-02-jwst-unearth mysterious-ancient-galaxy.html
[16] de Broglie, Louis Victor. "On the Theory of Quanta" (PDF). Foundation of Lou-is de Broglie (English translation by A.F. Kracklauer, 2004. ed.). Retrieved 25 February 2023.
[17] Einstein, Albert; Podolsky, Boris; Rosen, Nathan (1935). "Can
Quan-tum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality Be Considered
Complete?". Phys. Rev. 47 (10): 777-780. Bibcode:1935PhRv...47..777E.
doi:10.1103/PhysRev.47.777.
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.47.777
Figures Left to right - Top Row
Figure 1 Dimensions - energy leaves any dimensionless point at 90 degrees to a tangent
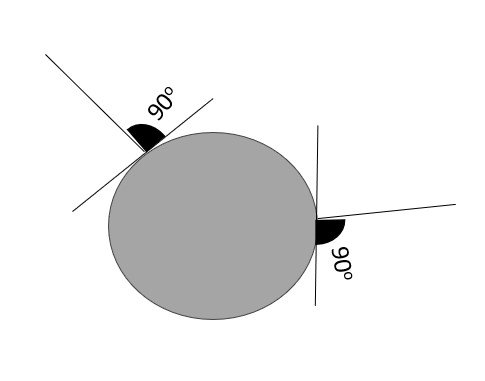
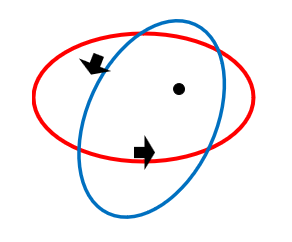
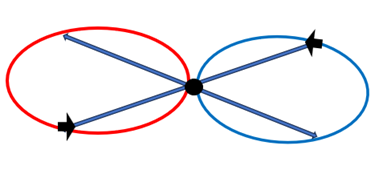
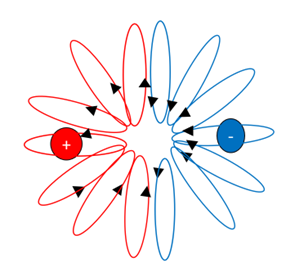
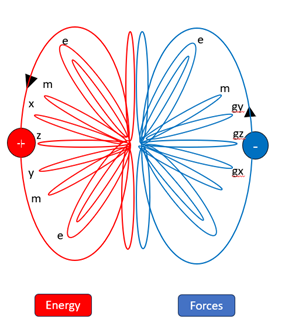
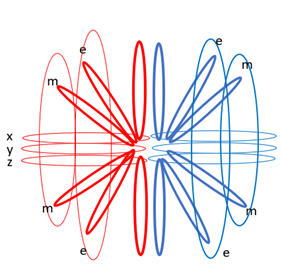
Above Left to right
Figure 3 A multidimensional energy-force structure develops
Figure 4 External electromagnetic orbits develop due to congestion.
Figure 5 Spatial dimensions are compressed towards the temporal axis by external compression of electromagnetic orbits
Below 1st Row Left to Right
Figure 6 Gravity according to TDSER
Figure 7 Development of charge within a quantum pole under extreme compression.
Figure 8 Compressive forces push dimensional forces inside particle orbits
Bottom row - Left to right
Figure 9 The Russian doll of concentric particle orbits
Figure 10 Potential charges within particle orbits
Figure 11 Particle with electrostatic orbits passing through background dimensional energy orbits and TDSER
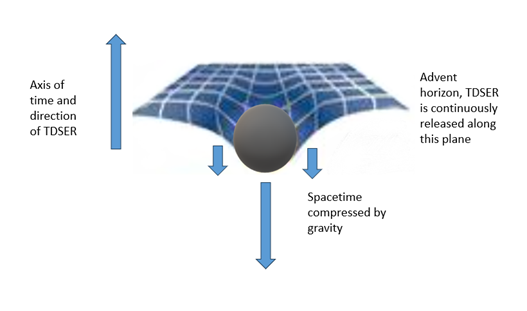
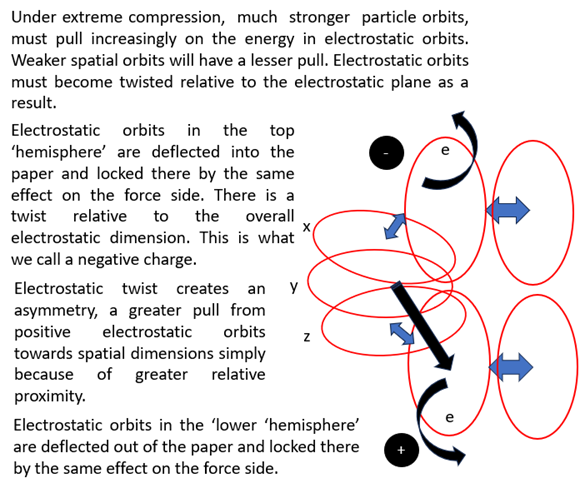
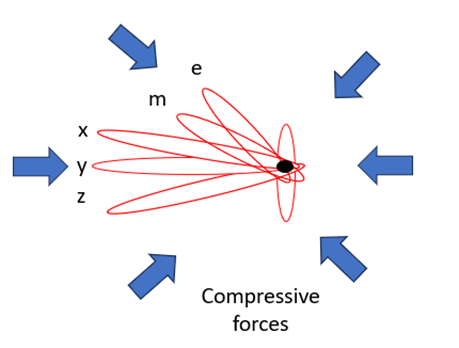
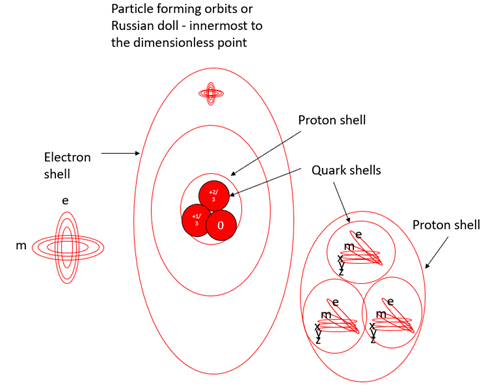
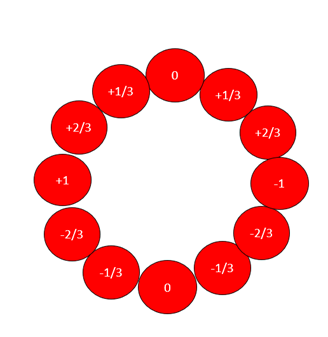
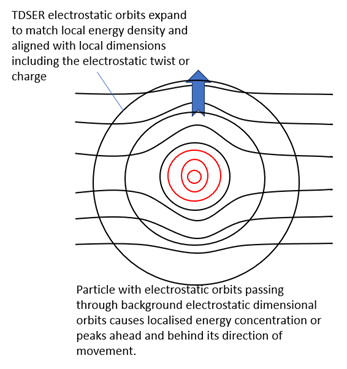
Figure 12 Side view of negatively charged particle relative to the electrostatic plane.
definition of a virtual messenger particle.
Figure 13 The TARDIS+
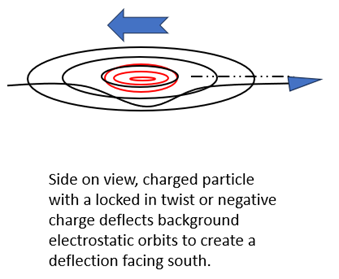
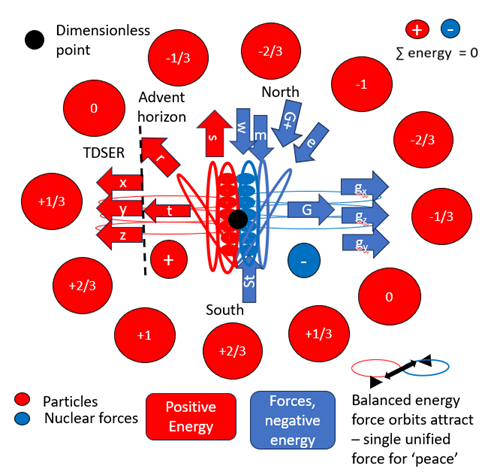
Everything
This article is based on the authors book "Everything" published February 2024 as an e book or paperback on amazon. Follow the links below: